Convolution of 3D Arrays using the Fourier Transform
convFFT.RdConvolve a three-dimensinal array with another three-dimensional arry using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT).
convFFT(A, B, C, FFTA = NULL)Arguments
| A | is a three-dimensional array (“the template”). |
|---|---|
| B | is a three-dimensional array (“the target”). |
| C | is a vector of length three (the center of “the template”). |
| FFTA | is the three-dimensional Fourier transform of |
Value
A three-dimensional array, the same dimension as the input arrays, that is the convolution of the “target” to the “template” at all spatial locations.
Details
The arrays \(A\) and \(B\) are transformed into the Fourier domain and multiplied together (equivalent to a convolution in the image domain across all spatial locations simultaneously).
References
Briggs, W.L. and Henson, V.E. (1995) The DFT: An Owner's Manual for the Discrete Fourier Transform, SIAM: Philadelphia.
See also
Author
Brandon Whitcher bwhitcher@gmail.com
Examples
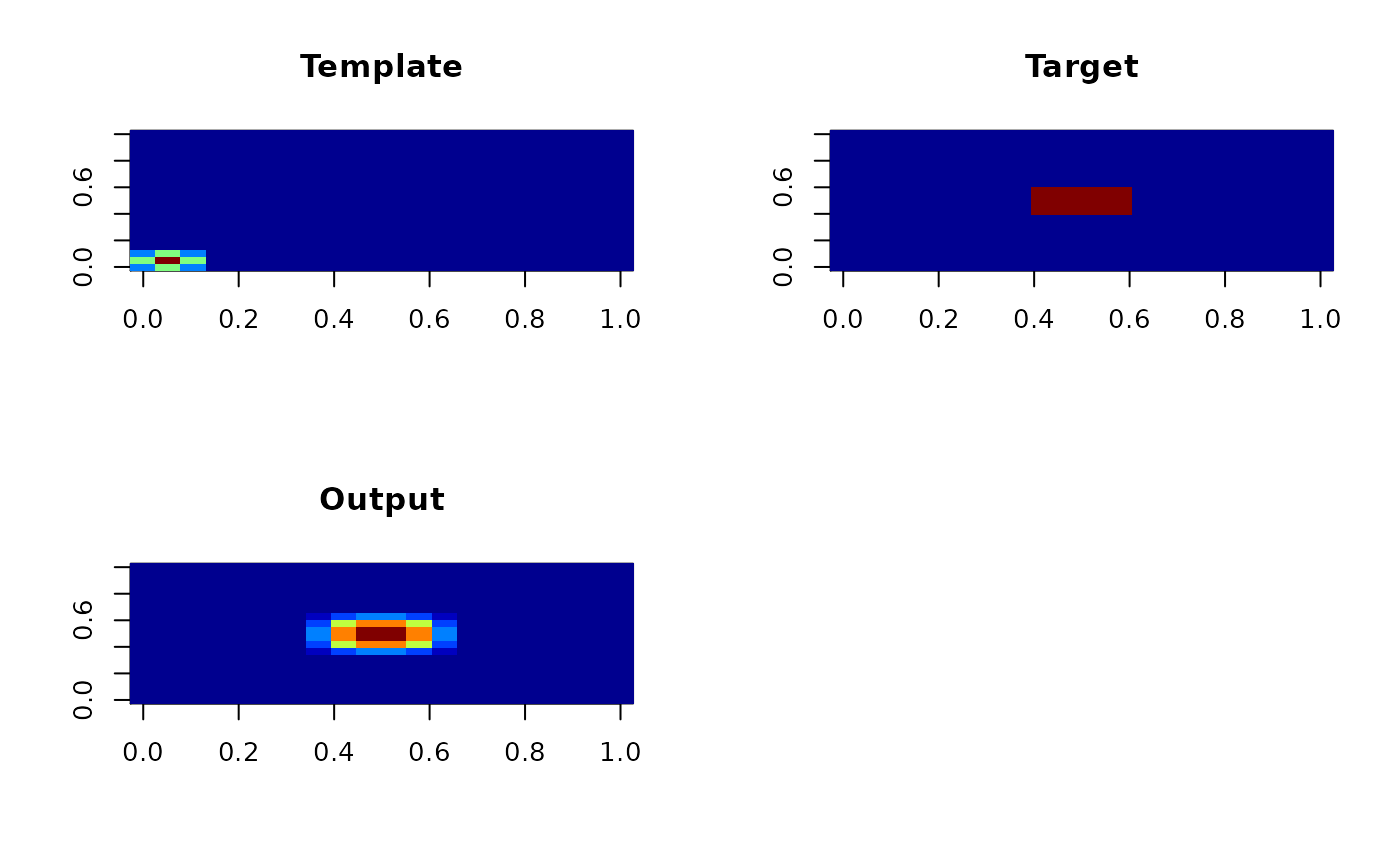
cube <- array(0, c(20,20,1))
cube[9:12,9:12,1] <- 1
tkernel <- array(0, c(20,20,1))
tkernel[,,1] <- c(.5, 1, .5, rep(0,20-3)) %o% c(.5, 1, .5, rep(0,20-3))
tcenter <- findCenter(ifelse(tkernel > 0, TRUE, FALSE))
out <- convFFT(tkernel, cube, tcenter)
out[8:13,8:13,1] ## text output
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6]
#> [1,] 0.25 0.75 1 1 0.75 0.25
#> [2,] 0.75 2.25 3 3 2.25 0.75
#> [3,] 1.00 3.00 4 4 3.00 1.00
#> [4,] 1.00 3.00 4 4 3.00 1.00
#> [5,] 0.75 2.25 3 3 2.25 0.75
#> [6,] 0.25 0.75 1 1 0.75 0.25
par(mfrow=c(2,2)) ## graphic output
image(drop(tkernel), col=oro.nifti::tim.colors(), main="Template")
image(drop(cube), col=oro.nifti::tim.colors(), main="Target")
image(drop(out), col=oro.nifti::tim.colors(), main="Output")